A failover cluster is a group of independent systems (nodes) that work together to ensure continuous database availability. This failover cluster setup contains multiple nodes that share a common storage system. If any of the nodes fail, the SQL server services are automatically transferred from a failed node to another node in a cluster. After making a cluster move from one server to another, you can face inconsistency issues in the database. In this article we’ll discuss methods to recover MSSQL database after a cluster failover. To perform the failover manually from one node to another, you can read this article.
How to Determine the Causes behind Consistency Errors in SQL Server Database?
After a cluster failover, you may fail to access the SQL database or experience random database consistency errors or issues. To find out what has caused database consistency errors in the Database, you can run the DBCC CHECKDB command. This command can check the overall integrity of the database. It checks inconsistencies in the database and also checks corruption in tables, data pages, and indexes.
Run the below CHECKDB command to check corruption in the SQL database:
DBCC CHECKDB ‘database_name’;
If the command finds corruption, it will return consistency errors, along with error message with description and also recommend the repair option to fix the issues.
Methods to recover the MSSQL Database after a cluster failover:
If there are inconsistency issues in the MS SQL then follow the below methods:
1- Restore your Backup file
If the SQL database is corrupted, or damaged, you can recover the database from the backup (.bak) file. You can restore backup file using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). SSMS is an effective tool with a user-friendly interface to manage SQL database.
Here are the steps to restore SQL database from a backup file using SSMS:
- Open SSMS and connect to the instance of SQL Server (in which your database is saved).
- Go to Object Explorer and click the Server Name to expand the Server tree.
- Navigate to Databases and open the database you want to restore in SQL Server.
- Right-click the Database and then click Restore Database.
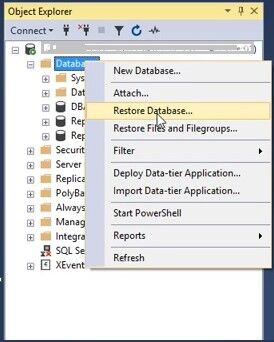
- The Restore Database window is displayed. On the General page, under the Source section, select any of these options:
- Choose the Database option and then select the database you want to restore from the dropdown list.
- Choose the Device option and then click the ellipses (…) to find your backup file.
- From the ‘Select backup devices‘ window, choose File as backup media, and then click Add.
- Locate and select the .BAK file you want to restore and then click OK.
- After the “restore of database completed successfully’’ message pops up, click OK.
2- Run DBCC CHECKDB with Minimum Repair Option
If restoring from the backup is not possible, try running the DBCC CHECKDB command with the minimum repair option to fix the consistency errors in SQL database.
The “DBCC CHECKDB REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS” is the minimum repair level that you can attempt to resolve the corruption errors in the SQL database. But the REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS option, as the name implies, can lead to data loss. Basically, the repair option may deallocate data (such as rows, pages, or series of pages), while resolving the error. This deallocated data cannot be recovered. So you can create a backup before executing REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS, and also, make sure you have all permissions and privileges on the database.
Here are the steps to repair SQL database using the DBCC CHECKDB REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS command:
Step 1- First set the database in SINGLE_USER mode. Here’s how to do this:
- In SSMS, in Object Explorer, connect to an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine and then expand that instance.
- Right-click on the database whose mode you want to change and click Properties.
- In the Database Properties dialog box, click Options.
- Under options, scroll down to State.
- Under State, click Restrict Access option, select SINGLE_USER and click OK.
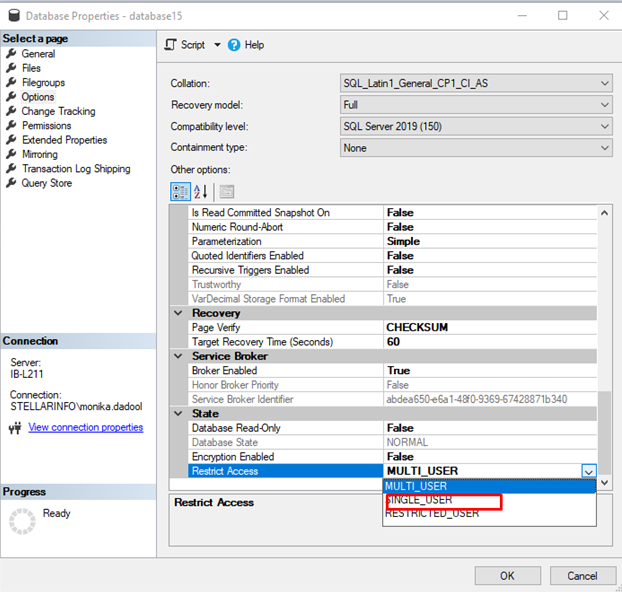
The SINGLE_USER mode prevent other users from changing the data during the repair process.
Step 2- After setting the database to SINGLE_USER mode, run the command with the REPAIR option recommended by DBCC CHECKDB command.
DBCC CHECKDB (N ’Dbtesting’, REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS) WITH ALL_ERRORMSGS, NO_INFOMSGS;
GO
Step 3- Next, again set the database to Multi-user mode by using the below command:
ALTER DATABASE Dbtesting SET MULTI_USER
3- Use a professional MS SQL Database Repair Tool:
To repair the MS SQL database quickly and with complete integrity and precision, you can download and use an advanced MS SQL repair tool such as Stellar Repair for MS SQL. This advanced tool can quickly repair damaged or corrupted MDF/NDF files and save all data to a new SQL database file with high precision. The tool also recovers all data, including deleted items from the damaged SQL database file. It can resolve many errors encountered while accessing the database in MS SQL, including DBCC CHECKB consistency errors like 823, 824, 829, 2508, 2511, 8993, and 7995, etc.
Features of Stellar Repair for MSSQL
- Repairs both MDF and NDF files with complete precision.
- Intuitive and user-friendly GUI.
- Supports recovery of all database objects, including tables, indexes, stored procedures, keys, and triggers.
- Restores deleted records from corrupt database.
- Supports selective recovery of database objects.
- Saves recovered SQL database data in a new database, live database, or other formats, including HTML, XLS, and CSV.
- Supports MS SQL Server 2022, MS SQL Server 2019, MS SQL Server 2017, and earlier versions.
- Supports recovery of compressed SQL database.
- Compatible with both Windows and Linux operating systems
Conclusion
You can encounter consistency issues in SQL database while working on a cluster failover environment or after a cluster failover. Whatever the situation, if your database is corrupted, then you can restore the SQL database. In this article, we’ve shared some solutions to recover the MS SQL database. You can use a professional SQL repair tool like Stellar Repair for MS SQL to repair damaged or corrupt SQL databases, irrespective of the level of damage, corruption, or size. You can restore all the data from corrupt SQL files with complete integrity and precision.
Pingback: Methods to Restore SQL Database if Backup File is Corrupted
Comments are closed.